Context-aware
Mobile Crowdsensing in Mobile Social Networks
Download
| Documentation | Examples
of Code | Publications
| Demos&Posters
|
Introduction
Mobile crowdsensing aims to
provide a mechanism to involve participants from the general public to
efficiently and effectively contribute and utilize context-related sensing data
from their mobile devices in solving specific problems in collaborations. The
wide availability of sensing modules in mobile devices enables social
networking services to be accessed and extended to incorporate location based
services, media tag services, etc. Therefore, there is growing interest in
fusing social networking services with real-world sensing, such as
crowdsensing. Mobile social
networks (MSNs) not only can provide an ideal and ubiquitous platform to
enable mobile users to participate in crowdsensing, but can also help to
improve the context-awareness of mobile applications and better assist users in
mobile crowdsensing by analyzing and utilizing their social contexts.
A number of research works have
identified that crowdsensing in MSN can be effectively used for many purposes
and bring huge economic benefits, e.g., vehicular social networks (VSNs) in
transportations like† transportation efficiency, green transportation, smart ridesharing, safe driving (SAfeDJ is available in Google Play now!); smart city; and crisis management. Our projects
target to explore the cutting edge challenges of mobile crowdsensing in MSNs
and provide systematic solutions, so as to facilitate the real-world deployment
of different context-aware mobile crowdsensing applications.
Mobile Ecosystem of Context-aware Mobile
Crowdsensing
In this work, we proposes a
multi-dimensional context-aware social network architecture, which aims to
provide a mobile ecosystem to enable context-awareness in the development and
utilization of mobile crowdsensing applications. This mobile ecosystem is constructed
to provide context-awareness capabilities for different roles (i.e., users or
developers) in the system and facilitate the interactions between them.
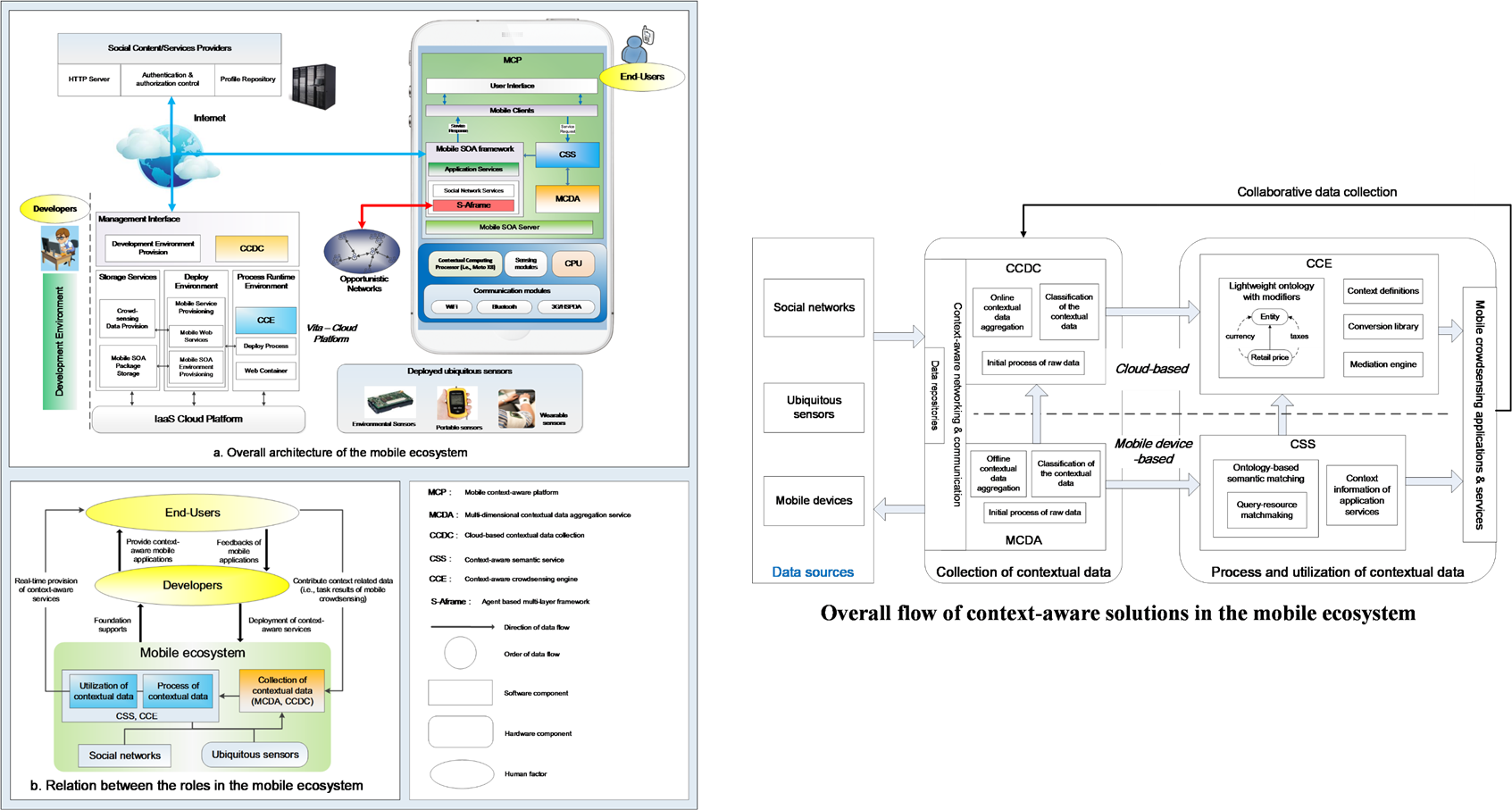
This system can ease the
development of context-aware mobile applications and enable context-aware
mobile crowdsensing considering environmental, personal and social information.
We present a flow of context-aware solution designed on this system, and
highlight the orchestrations and the advantages of different context-aware
schemes in the system for different types of users (requesters and
participants) in mobile crowdsensing.
Vita: A Crowdsensing-oriented Mobile Cyber
Physical System
As a prominent subcategory of
cyber-physical systems, mobile cyber-physical systems could take advantage of
widely used mobile devices such as smartphones as a convenient and economical
platform that facilitates sophisticated and ubiquitous mobile sensing
applications between humans and the surrounding physical world. This work
presents Vita, a novel mobile cyber-physical system for crowdsensing
applications, which enables mobile users to perform mobile crowdsensing tasks
in an efficient manner through mobile devices.
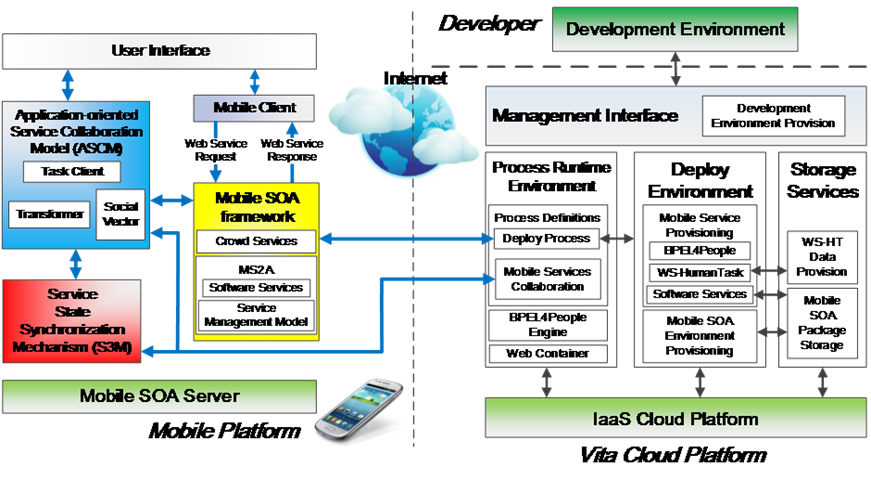
Vita provides a flexible and
universal architecture across mobile devices and cloud computing platforms by integrating
the service-oriented architecture with resource optimization mechanism for
crowdsensing, with extensive supports to application developers and end users.
The customized platform of Vita enables intelligent deployments of tasks
between human in the physical world, and dynamic collaborations of services
between mobile devices and cloud computing platform during run-time of mobile
devices with service failure handling support.
Our practical experiments show
that Vita performs its tasks efficiently with a low computation and
communication overhead on mobile devices, and eases the development of multiple
mobile crowdsensing applications and services. Also, we present a context-aware
mobile crowdsensing application Ė Smart
City developed on Vita to demonstrate the functionalities and practical
usage of Vita.
S-Aframe: Agent-based Multi-layer
Framework with Context-aware Semantic Service for Vehicular Social Networks
This work presents S-Aframe, an
agent based multi-layer framework with context-aware semantic service (CSS) to
support the development and deployment of context-aware applications for
vehicular social networks (VSNs) formed by in-vehicle or mobile devices used by
drivers, passengers, and pedestrians.
The programming model of the
framework incorporates features that support collaborations between mobile
agents to provide communication services on behalf of owner applications, and
service (or resident) agents to provide application services on mobile devices.
Using this model, different self-adaptive applications and services for VSNs
can be effectively developed and deployed.

Built on top of the mobile
devicesí operating systems, the framework architecture consists of framework service
layer, software agent layer and owner application layer. Integrated with the
proposed novel CSS, applications developed on the framework can autonomously
and intelligently self-adapt to rapidly changing network connectivity and
dynamic contexts of VSN users.

A practical implementation and
experimental evaluations of S-Aframe are presented to demonstrate its
reliability and efficiency in terms of computation and communication
performance on popular mobile devices. In addition, a VSN-based smart ride application is developed to
demonstrate the functionality and practical usefulness of S-Aframe.
SAfeDJ: A Crowd-Cloud Co-design Approach to
Situation-aware Music Delivery for Drivers †(available in Google Play now!)
Driving is an integral part of
our everyday lives, but it is also a time when people are uniquely vulnerable.
Previous research has demonstrated that not only does listening to suitable
music while driving not impair driving performance, but it could lead to an
improved mood and a more relaxed body state, which could improve driving
performance and promote safe driving significantly. In this work, we propose SAfeDJ, a
smartphone-based situation-aware music recommendation system, which turns driving
into a safe and enjoyable experience. SAfeDJ aims at helping drivers to
diminish fatigue and negative emotion.
††
††††††††††††††††††† ††††††
††††††
Its design is based on novel
interactive methods, which enable in-car smartphones to orchestrate multiple
sources of sensing data and the driversí social context, in collaboration with
cloud computing to form a seamless crowdsensing solution. This solution enables
different smartphones to collaboratively recommend preferable music to drivers
according to each driverís specific situations in an automated, precise and
intelligent manner.
Practical experiments of SAfeDJ have
proved its effectiveness in music-mood analysis, and mood-fatigue detections of
drivers with reasonable computation and communication overheads on smartphones.
Also, our user studies have demonstrated that SAfeDJ helps to decrease 49.09%
fatigue degree and 36.35% negative mood degree of drivers compared to
traditional smartphone-based music player under the same driving situations.
†Social Drive: A Crowdsourcing-based Vehicular
Social Networking System for Green Transportation
Social Drive is a novel
crowdsourcing-based vehicular social networking (VSN) system for green
transportation. Social Drive integrates the standard vehicular On-Board
Diagnostics (OBD) module, leverages the advantages of cloud computing and
popular social networks, and incorporates a novel rating mechanism about the
fuel economy of drivers. Based on these, Social Drive provides a user-friendly
mobile application on smartphones targeting drivers, which enables a seamless
and economic solution that promote driversí awareness of their driving
behaviors regarding fuel economy of specific trips. Our practical experiments
have demonstrated that Social Drive works efficiently with low battery
consumption and low networking overhead on popular mobile devices

People
The works were mainly done by Xiping Hu (email: xipingh@ece.ubc.ca) at The University of
British of Colombia, Canada, during Sep.
2011 - Aug. 2015. These were international collaboration projects, which
had been involving partners from global, such as The University of Hong Kong
and The Hong Kong Polygenic University in Hong Kong, Uppsala University in
Sweden, HEC Paris in France, University of Twente in Netherlands, East China
Normal University, Shanghai Jiaotong University and Tsinghua University in
China, Massachusetts Institute of Technology in USA, University of Cambridge
and University of Sussex in UK, University of New Brunswick in Canada, Auckland
University of Technology in New Zealand, TELUS and IBM Canada, Microsoft and
IBM China etc.
|
|